You are invited to attend our weekly ECE Graduate Seminar.
All lectures to be held at 3:00pm on Fridays online at https://vs.prod.odu.edu/kvs/zoom/?cid=202120_ECE731831GraduateSeminarSpring2022VS_96353
For more information, contact Dr. Chung Hao Chen at (757) 683-3475 or email cxchen@odu.edu.
Friday, February 25, 2022 Seminar Topic:
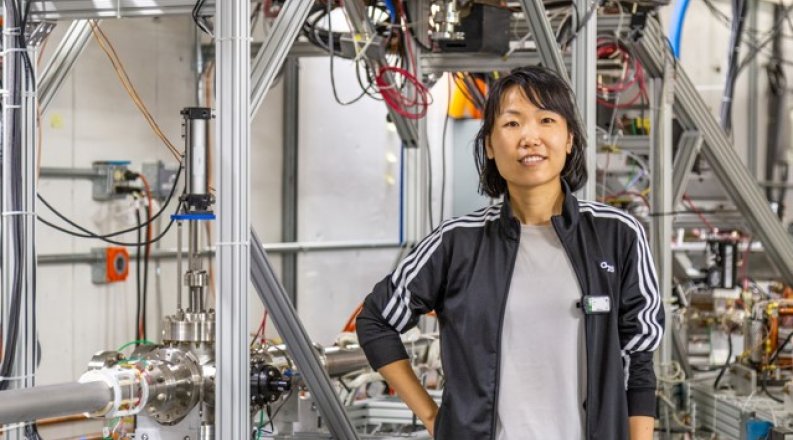
"Irradiation of 1,4-dioxane for Wastewater Remidiation" by Xi Li, Ph.D. Candidate in the Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering at Old Dominion University
Abstract:
Electron beam (e-beam) irradiation produces both, reducing and oxidizing species which facilitate the reduction of contaminants found in wastewater. To investigate the impact of electron beam on 1,4-dioxane, a widely used solvent which has been declared as a probable human carcinogen by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), an e-beam irradiation beamline was designed and commissioned at the Upgraded Injector Test Facility (UITF) at Jefferson Lab. Here, wastewater samples can be irradiated with a beam energy up to 10 MeV. A beam spot with a diameter of ~5 cm was produced at the target location using a solenoid and a pair of raster coils. Electron beam irradiation studies were performed using 1,4-dioxane in three different matrices, ultra-pure water, secondary effluent wastewater and granular activated carbon (GAC) filtered secondary effluent wastewater, and for two concentrations, ~10 μg/L and ~100 μg/L. The concentration of 1,4-dioxane after irradiation was measured as a function of dose.
Bio:
Xi Li is a Ph.D. candidate in the Electrical and Computer Engineering department at ODU. She received her BS degree in Physics from Wuhan University, China, and MS degree in Engineering from China Academy of Engineering Physics, China. Currently, she is working toward her dissertation under the supervision of Dr. H. Baumgart in ODU and Dr. S. Wang, Dr. G. Ciovati in Jlab. Her research interests include interaction of electron beam on/into material, electron beam transportation, electron accelerator design, wastewater treatment.